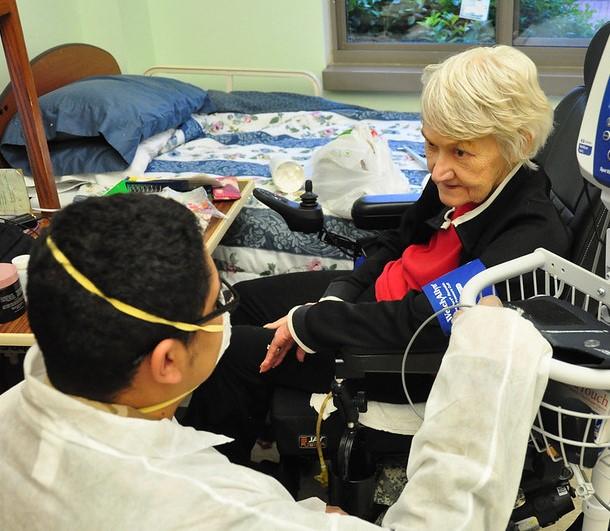
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on the healthcare system worldwide, and nursing homes have been at the forefront of this crisis. Nursing homes are designed to provide a safe and secure environment for the elderly and other vulnerable individuals who require around-the-clock medical care and support. However, since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, nursing homes have been struggling to keep their residents safe and healthy. In this blog post, we will discuss the adverse effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on nursing homes.
Increased Risk of Infection

Nursing homes have always been at risk of infections, but the COVID-19 pandemic has increased this risk significantly. Elderly residents in nursing homes are more susceptible to infections due to weakened immune systems, chronic health conditions, and advanced age. The COVID-19 virus is highly contagious, and nursing homes are among the most vulnerable settings for outbreaks. Nursing homes are often overcrowded, with residents sharing rooms and communal spaces. This makes it easier for the virus to spread from one person to another.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that COVID-19 has disproportionately affected nursing home residents, accounting for over 40% of all COVID-19 deaths in the United States. Furthermore, the CDC has noted that outbreaks in nursing homes can spread quickly and be difficult to contain, often resulting in severe illness and death among residents.
Shortage of Staff

The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in a shortage of staff in nursing homes. Many staff members have contracted the virus, and some have even died from it. This has resulted in a shortage of nurses, doctors, and other healthcare workers in nursing homes. The shortage of staff has put a strain on the remaining workers, who are forced to work longer hours and take on additional responsibilities. This can lead to burnout and increased stress levels among staff members, which can ultimately affect the quality of care provided to residents.
Isolation and Loneliness

The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in widespread isolation and loneliness among nursing home residents. Due to restrictions on visitation, residents have been unable to see their loved ones in person for extended periods. This has resulted in feelings of loneliness, depression, and anxiety. The lack of social interaction and mental stimulation can lead to cognitive decline and other health issues in elderly residents.
According to a report by the American Association of Retired Persons (AARP), isolation and loneliness can have severe consequences for nursing home residents. The report notes that social isolation can increase the risk of mortality, depression, and cognitive decline. Furthermore, the report suggests that social isolation can exacerbate existing health conditions, including hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease.
Financial Strain

The COVID-19 pandemic has also had a significant financial impact on nursing homes. Many nursing homes have been forced to close due to the pandemic, resulting in job losses for staff members and displacement for residents. Nursing homes that remain open have had to implement expensive infection control measures, including the purchase of personal protective equipment (PPE) and hiring additional staff. These additional costs have put a strain on the already limited resources of many nursing homes.
According to a report by the National Center for Assisted Living, nursing homes have experienced significant financial losses due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The report notes that nursing homes have had to spend more money on PPE and cleaning supplies, and many have lost revenue due to a decrease in admissions.
Inadequate Access to Testing and Treatment
Nursing home residents require regular testing and medical care to ensure their health and safety. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in a shortage of testing and treatment resources. Many nursing homes have reported difficulty in obtaining testing supplies and have had to rely on limited resources. This has made it difficult to detect and prevent the spread of COVID-19 in nursing homes.
Furthermore, some nursing homes have reported difficulty in obtaining adequate medical care for their residents. The pandemic has resulted in a shortage of medical professionals and hospital beds, making it difficult for nursing home residents to receive timely and appropriate medical care.
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on nursing homes. The increased risk of infection, shortage of staff, isolation and loneliness, financial strain, and inadequate access to testing and treatment have all contributed to the adverse effects of the pandemic on nursing homes. It is essential that nursing homes receive adequate support and resources to ensure the safety and well-being of their residents during these challenging times.
Some of the measures that can be taken to mitigate the impact of the pandemic on nursing homes include increased access to testing and treatment, adequate staffing levels, increased infection control measures, and improved access to mental health services for residents. Additionally, there should be a focus on ensuring that nursing home residents have access to regular social interaction and mental stimulation to reduce the risk of loneliness and cognitive decline.
It is also essential that nursing homes receive adequate funding to cover the additional costs associated with the pandemic. This can be achieved through government funding, private donations, and community support. By providing nursing homes with the necessary resources and support, we can help to mitigate the adverse effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on nursing homes and ensure the safety and well-being of their residents.

Gut Health for Yoginis: Enhancing Your Practice with Fiber and Ancestral Nutritions Fibre Clenz
Share on facebook Facebook Share on twitter Twitter Share on linkedin LinkedIn Share on facebook Facebook Share on pinterest Pinterest Share on telegram Telegram Share
A Pillar of Strength in Golden Years: 10 Paths on How Regular Screenings Uphold Your Health
In the evocative voyage of life, the golden years emerge as a time to relish the fruits of decades of labor, to bask in the
Unlock the Secret to Sweet Dreams: 10 Ways of Enhancing Sleep Quality as You Age
Share on facebook Facebook Share on twitter Twitter Share on linkedin LinkedIn Share on pinterest Pinterest Share on telegram Telegram Share on whatsapp WhatsApp Share
Building Bridges, Not Walls: 10 Methods of Mastering the Art of Cultivating Social Connections in the Golden Years
Share on facebook Facebook Share on twitter Twitter Share on linkedin LinkedIn Share on telegram Telegram Share on whatsapp WhatsApp Share on email Email Share
Navigating the Golden Years: 10 Ways to Achieve Emotional Wellness and Conquering Loneliness
Share on facebook Facebook Share on twitter Twitter Share on linkedin LinkedIn Share on pinterest Pinterest Share on telegram Telegram Share on whatsapp WhatsApp Share
Stay Brainy in Your Golden Years: 10 Fun Activities to Keep Your Mind Sharp and Engaged!
Hello, brain buffs! Aging might be inevitable, but letting our minds turn to mush? No way, José! Time to boot up those brain cells and